The Use of Cialis in Hepatic Impairment Patients
Cialis is a drug that contains tadalafil. It relaxes muscles in the blood vessels and enhances the flow of blood to certain areas of the body.
Cialis assists to treat erectile dysfunction (impotence) and benign prostatic hypertrophy symptoms. Impotence is a disease when men can’t have normal erections necessary for satisfactory sexual intercourse. Please note that Cialis has no effect on the libido, the sperm activity or the ability to fertilize an egg. The drug expands the blood vessels of the penis during sexual arousal. As a result, the blood circulation in the penis is enhanced and this, in turn, promotes the onset of a stable erection.
Important Information
Some medicines when used together with Cialis can cause dangerous effects. Thus, before taking Cialis tell your physician about the medicines you’re taking.
If you use a nitrate drug to treat heart problems, you should avoid using Cialis at the same time. Otherwise, it will cause a dangerous decrease in blood pressure.
If your erection hurts or lasts more than 4 hours, immediately contact your doctor. A protracted erection can damage your genital organ.
Stop using Cialis if you have a sudden vision loss.
Do not take Cialis in the following cases:
- You are taking drugs containing any organic nitrates.
- You have an increased sensitivity to components of Cialis. An allergic reaction to tadalafil may appear in a rash, itching, swelling of face or lips, shortness of breath. If you have these symptoms, be sure to tell your doctor.
- Before taking Cialis, you should immediately inform your physician if any of the following is true:
- You have an acute liver failure. If you suffer from severe hepatic impairment, you should take precautions when taking Cialis.
- You have renal failure. Patients with renal insufficiency, who take Cialis for sexual arousal and stimulation, can have moderate back pain.
- You suffered a heart attack within the past 90 days or have had unstable, chronic heart failure, uncontrolled cardiac arrhythmias, hypotension, uncontrolled hypertension, stroke, and myocardial infarction within the last 6 months.
- You are predisposed to priapism, multiple myelomas, sickle cell disease or leukemia.
- You have an anatomical malformation of the penis (cavernous fibrosis, angulation or Peyronie’s disease).
Cialis should not be combined with other agents intended to treat erectile dysfunction.
How to Take Cialis?
Only a physician can decide what dosage of Cialis you should take. Usually, it is taken only once a day at least 16 minutes before the sexual intercourse. Follow all the instructions of your doctor and don’t take the drug in larger or smaller quantities or longer than it is recommended. Swallow a whole pill with a little of water with or without food.
Patients can try to perform a sexual intercourse at any time within 36 hours after taking the pill. Cialis helps achieve an erection only if there is sexual excitement. If there is no sexual arousal, Cialis will not lead to the onset of an erection.
Effects of tadalafil start at different times for different people, but as it was mentioned above, the minimum time needed for the pill to start acting is 16 minutes before the intercourse. Drinking alcohol might have effects on the action of Cialis and can lead to the occurrence of side effects. If after taking Cialis, you don’t have an erection or the duration of an erection is not sufficient to complete a sexual intercourse, you should seek medical advice.
Cialis Side Effects
Like many other medicines, Cialis can cause undesirable side effects. They are usually moderately expressed and don’t stay for long. The most common side effects are a headache and indigestion. Also, there might be back pain, myalgia, dizziness, stuffy nose, and changes in vision (change of color of objects, increased brightness of light or blurred vision).
If after taking this medicine you have any of these side effects, be sure to consult a doctor. Your doctor may make the dose smaller. If you have any undesirable side effects, which are not indicated in the instructions, ask your physician or pharmacist for advice.
Stop using Cialis and get emergency help in the following cases:
- Erection is painful and lasts more than 4 hours
- Sudden changes in vision or its loss
- Symptoms of a heart attack
- Ringing in your ears or loss of hearing
- Swelling in your ankles, feet, or hands
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Seizure
- A light-headed feeling
Since there is no data about how the use of Cialis affects patients who suffer from severe hepatic impairment, caution is needed when prescribing the drug to this group of patients.
About Hepatic Impairment
Liver impairment is a clinical syndrome that occurs during a partial dysfunction of the liver, i.e. when the liver is not able to fully recover and participate in metabolism.
The role of the liver in metabolism is immense. It controls absolutely all of its processes, and thus any disruption in the body is invariably accompanied by hepatic insufficiency.
Causes of Disease
There are many reasons that can lead to the development of hepatic impairment. They include:
- Infectious and parasitic diseases (hepatitis B, C, and E). In rare cases, hepatic impairment can be caused by herpes, adenovirus, yellow fever, and tuberculosis.
- Chronic diseases of the liver (cirrhosis) and other organs (dysfunctionality of the cardiovascular and endocrine systems).
- An intoxication caused by drugs (especially antibiotics), alcohol, and poisonous mushrooms.
- Biliary tracts obstruction, causing a number of pathological processes in the liver cells (bile hypertension and as a result, poor circulation, and oxygen exchange).
- Various injuries, burns, and shock situations.
Regardless of the causes that lead to the development of hepatic impairment, this syndrome manifests spontaneously and progresses rapidly because the liver cells are very sensitive to the lack of oxygen.
Symptoms of Hepatic Impairment
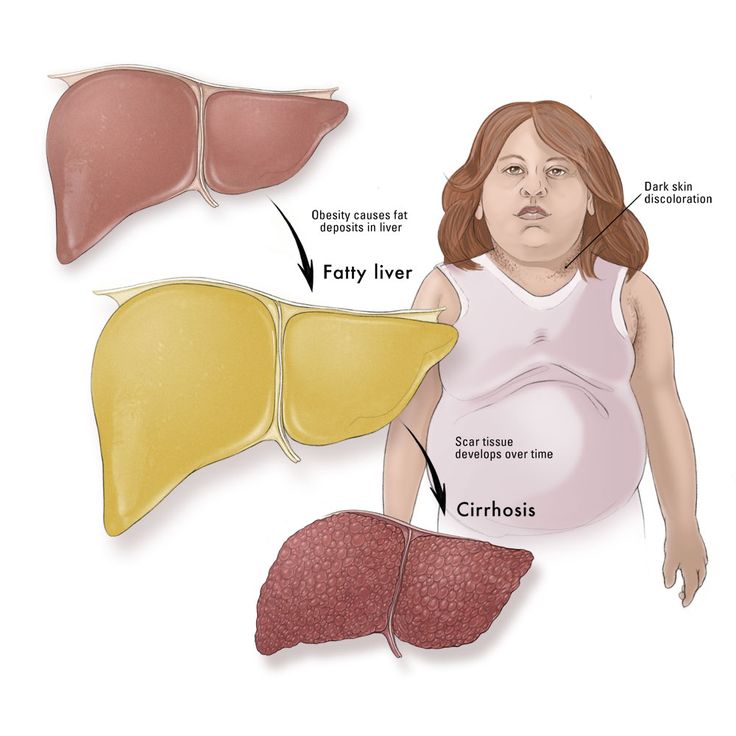
Hepatic impairment is mainly determined by two pathological processes: cholestasis and hepatic tissue necrosis.
In the first case, the obstruction of the biliary tracts and loss of normal bile excretion leads to jaundice. It is the most distinctive and visible manifestation of the liver disease. It may be acute and chronic. The degree of severity of jaundice can vary from bright to almost imperceptible pigmentation type.
In the second case, many hazardous processes begin. Hepatocellular insufficiency not only leads to fever, but also to a variety of disorders of the cardiovascular system (change in blood circulation, tachycardia, hypertension, and hypotension) and the work of the gastrointestinal tract.
The development of all the symptoms described above eventually leads to absolute fibrosis (liver replacement by connective tissue) and cirrhosis.
Cialis Use in Hepatic Impairment
There are specific dose recommendations of Cialis for the patients with hepatic impairment.
Use of Cialis on demand:
- The recommended Cialis dose for the cure of erectile dysfunction on demand is 10 mg before the sexual intercourse.
- Patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment should take a dose of 10 mg.
- There is very little data on the safety of Cialis in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Thus, if prescribed, the doctor should undertake a careful individual risk evaluation.
- There is no information about the dosing of higher than 10 mg to patients with hepatic impairment.
- Use of Cialis once a day in men with hepatic impairment:
- Daily use of Cialis both for benign prostatic hyperplasia and erectile dysfunction has not been evaluated in patients with hepatic impairment. Thus, if prescribed, the prescribing doctor should undertake a careful individual risk evaluation.


